Paramount Tax & Accounting Flint Hills Blog
Featured Articles June 2018 - Manhattan
Feature Articles
- Saving for Education: 529 Plans
- Tax Consequences of Crowdfunding
- Filing an Amended Return
- Tax Breaks for Businesses Hiring New Employees
- Seasonal Employees and Taxes
Tax Tips
- HSA Limits Increase for 2019
- New Scam Targets Non-resident Aliens
- What to do if you get a Letter from the IRS
- Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Program to End this Year
- Employer Credit for Family and Medical Leave
QuickBooks Tips
Saving for Education: 529 Plans
Many parents are looking for ways to save for their child's education and a 529 Plan is an excellent way to do so. Even better, is that thanks to the passage of tax reform legislation in 2017, 529 plans are now available to parents wishing to save for their child's K-12 education as well as college or vocational school. Here are some tips on saving for education, brought to you by our tax accountants Manhattan. Contact Paramount Tax & Accounting Flint Hills in Manhattan to learn more.
You may open a Section 529 plan in any state, and there are no income restrictions for the individual opening the account. Contributions, however, must be in cash and the total amount must not be more than is reasonably needed for higher education (as determined initially by the state). There may also be a minimum investment required to open the account, typically, $25 or $50.
Each 529 Plan has a Designated Beneficiary (the future student) and an Account Owner. The account owner may be a parent or another person and typically is the principal contributor to the program. The account owner is also entitled to choose (as well as change) the designated beneficiary.
Neither the account owner or beneficiary may direct investments, but the state may allow the owner to select a type of investment fund (e.g., fixed income securities), change the investment annually as well as when the beneficiary is changed. The account owner decides who gets the funds (can pick and change the beneficiary) and is legally allowed to withdraw funds at any time, subject to tax and penalties (more about this below).
Unlike some of the other tax-favored higher education programs such as the American Opportunity and Lifetime Learning Tax Credits, federal tax law doesn't limit the benefit only to tuition. Room, board, lab fees, books, and supplies can be purchased with funds from your 529 Savings Account. Individual state programs could have a more narrow definition, however, so be sure to check with your particular state.
Tax-free Distributions
Distributions from 529 plans are tax-free as long as they are used to pay qualified higher education expenses for a designated beneficiary. Distributions are tax-free even if the student is claiming the American Opportunity Credit, Lifetime Learning Credit, or tax-free treatment for a Section 530 Coverdell distribution--provided the programs aren't covering the same specific expenses. Qualified expenses include tuition, required fees, books, supplies, equipment, and special needs services. For someone who is at least a half-time student, room and board also qualify. Also, starting in 2018, "qualified higher education expenses" include up to $10,000 in annual expenses for tuition in connection with enrollment or attendance at an elementary or secondary public, private, or religious school.
Note: Qualified expenses also include computers and related equipment used by a student while enrolled at an eligible educational institution; however, software designed for sports, games, or hobbies does not qualify unless it is predominantly educational in nature.
Federal Tax Rules
Income Tax. Contributions made by the account owner or other contributor are not deductible for federal income tax purposes, but many states offer deductions or credits. Earnings on contributions grow tax-free while in the program. Distribution for a purpose other than qualified education is taxed to the one receiving the distribution. In addition, a 10 percent penalty must be imposed on the taxable portion of the distribution, comparable to the 10 percent penalty in Section 530 Coverdell plans. Also, the account owner may change the beneficiary designation from one to another in the same family. Funds in the account roll over tax-free for the benefit of the new beneficiary.
Gift Tax. For gift tax purposes, contributions are treated as completed gifts even though the account owner has the right to withdraw them - thus they qualify for the up-to-$15,000 annual gift tax exclusion. One contributing more than $15,000 may elect to treat the gift as made in equal installments over that year and the following four years, so that up to $75,000 can be given tax-free in the first year.
Estate Tax. Funds in the account at the designated beneficiary's death are included in the beneficiary's estate - another odd result, since those funds may not be available to pay the tax. Funds in the account at the account owner's death are not included in the owner's estate, except for a portion thereof where the gift tax exclusion installment election is made for gifts over $15,000. For example, if the account owner made the election for a gift of $75,000 in 2018, a part of that gift is included in the estate if he or she dies within five years.
Tip: A Section 529 program can be an especially attractive estate-planning move for grandparents. There are no income limits, and the account owner giving up to $75,000 avoids gift tax and estate tax by living five years after the gift, yet has the power to change the beneficiary.
State Tax. State tax rules are all over the map. Some reflect the federal rules, some quite different rules. For specifics of each state's program, see http://www.collegesavings.org.
Professional Guidance
Considering the differences among state plans, the complexity of federal and state tax laws, and the dollar amounts at stake, please call the office and speak to a tax and accounting professional before opening a 529 plan.
Tax Consequences of Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding websites such as Kickstarter, GoFundMe, Indiegogo, and Lending Club have become increasingly popular for both individual fundraising and small business owners looking for start-up capital or funding for creative ventures. The upside is that it's often possible to raise the cash you need but the downside is that the IRS considers that money taxable income. Here's what you need to know.
What is Crowdfunding?
Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project by gathering online contributions from a large group of backers. Crowdfunding was initially used by musicians, filmmakers, and other creative types to raise small sums of money for projects that were unlikely to turn a profit. Now it is used to fund a variety of projects, events, and products and in some cases, has become an alternative to venture capital.
There are three types of crowdfunding: donation-based, reward-based, and equity-based. Donation-based crowdfunding is when people donate to a cause, project, or event. GoFundMe is the most well-known example of donation-based crowdfunding with pages typically set up by a friend or family member ("the agent") such as to help someone ("the beneficiary") pay for medical expenses, tuition, or natural disaster recovery.
Reward-based crowdfunding involves an exchange of goods and services for a monetary donation, whereas, in equity-based crowdfunding, donors receive equity for their contribution.
Are Crowdfunding Donations Taxable?
This is where it can get tricky. As the agent, or person who set up the crowdfunding account, the money goes directly to you; however, you may or may not be the beneficiary of the funds. If you are both the agent and the beneficiary you would be responsible for reporting this income. If you are acting as "the agent", and establish that you are indeed, acting as an agent for a beneficiary who is not yourself, the funds will be taxable to the beneficiary when paid--not to you, the agent. An easy way to circumvent this issue is to make sure when you are setting up a crowdfunding account such as GoFundMe you clearly designate whether you are setting up the campaign for yourself or someone else.
Again, as noted above, as the beneficiary, all income you receive, regardless of the source, is considered taxable income in the eyes of the IRS--including crowdfunding dollars. However, money donated or pledged without receiving something in return may be considered a "gift." As such the recipient does not pay any tax. Up to $15,000 per year per recipient may be given by the "gift giver."
Let's look at an example of reward-based crowdfunding. Say you develop a prototype for a product that looks promising. You run a Kickstarter campaign to raise additional funding, setting a goal of $15,000 and offer a small gift in the form of a t-shirt, cup with a logo or a bumper sticker to your donors. Your campaign is more successful than you anticipated it would be and you raise $35,000--more than twice your goal.
Taxable sale. Because you offered something (a gift or reward) in return for a payment pledge it is considered a sale. As such, it may be subject to sales and use tax.
Taxable income. Since you raised $35,000, that amount is considered taxable income. But even if you only raised $15,000 and offered no gift, the $15,000 is still considered taxable income and should be reported as such on your tax return--even though you did not receive a Form 1099-K from a third party payment processor (more about this below).
Generally, crowdfunding revenues are included in income as long as they are not:
- Loans that must be repaid;
- Capital contributed to an entity in exchange for an equity interest in the entity; or
- Gifts made out of detached generosity and without any "quid pro quo." However, a voluntary transfer without a "quid pro quo" isn't necessarily a gift for federal income tax purposes.
Income offset by business expenses. You may not owe taxes however, if your crowdfunding campaign is deemed a trade or active business (and not a hobby) your business expenses may offset your tax liability.
Factors affecting which expenses could be deductible against crowdfunding income include whether the business is a start-up and which accounting method (cash vs. accrual) you use for your funds. For example, if your business is a startup you may qualify for additional tax benefits such as deducting startup costs or applying part or all of the research and development credit against payroll tax liability instead of income tax liability.
Timing of the crowdfunding campaign, receipt of funds, and when expenses are incurred also affect whether business expenses will offset taxable income in a given tax year. For instance, if your crowdfunding campaign ends in October but the project is delayed until January of the following year it is likely that there will be few business expenses to offset the income received from the crowdfunding campaign since most expenses are incurred during or after project completion.
How do I Report Funds on my Tax Return?
Typically, companies that issue third-party payment transactions such as Amazon if you use Kickstarter, PayPal if you use Indiegogo, or WePay if you use GoFundMe) are required to report payments that exceed a threshold amount of $20,000 and 200 transactions to the IRS using Form 1099-K, Payment Card and Third Party Network Transactions. The minimum reporting thresholds of greater than $20,000 and more than 200 transactions apply only to payments settled through a third-party network; there is no threshold for payment card transactions.
Form 1099-K includes the gross amount of all reportable payment transactions and is sent to the taxpayer by January 31 if payments were received in the prior calendar year. Include the amount found on your Form 1099-K when figuring your income on your tax return, generally, Schedule C, Profit or Loss from Business for most small business owners.
Again, tax law is not clear on this when it comes to crowdfunding donations. Some third-party payment processors may deem these donations as gifts and do not issue a 1099-K. This is why it is important to keep good records of transactions relating to your crowdfunding campaign including a screenshot of the crowdfunding campaign (it could be several years before the IRS catches up) and documentation of any money transfers.
Don't Get Caught Short.
If you're thinking of crowdfunding to raise money for your small business or startup or for a personal cause, consult a tax and accounting professional first. Don't make the mistake of using all of your crowdfunding dollars on your project and then discovering you owe tax and have no money with which to pay it.
Filing an Amended Return
What should you do if you already filed your federal tax return and then discover a mistake? First of all, don't worry. In most cases, all you have to do is file an amended tax return. But before you do that, here is what you should be aware of when filing an amended tax return.
Taxpayers should use Form 1040X, Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, to file an amended (corrected) tax return.
An amended return cannot be e-filed. You must file the corrected tax return on paper. If you need to file another schedule or form, don't forget to attach it to the amended return.
An amended tax return should only be filed to correct errors or make changes to your original tax return. For example, you should amend your return if you need to change your filing status or correct your income, deductions or credits.
You normally do not need to file an amended return to correct math errors because the IRS automatically makes those changes for you. Also, do not file an amended return because you forgot to attach tax forms, such as W-2s or schedules. The IRS normally will mail you a request asking for those.
If you are amending more than one tax return, prepare a separate 1040X for each return and mail them to the IRS in separate envelopes. Note the tax year of the return you are amending at the top of Form 1040X. You will find the appropriate IRS address to mail your return to in the Form 1040X instructions.
If you are filing an amended tax return to claim an additional refund, wait until you have received your original tax refund before filing Form 1040X. Amended returns take up to 16 weeks to process. You may cash your original refund check while waiting for the additional refund.
If you owe additional taxes file Form 1040X and pay the tax as soon as possible to minimize interest and penalties. You can use IRS Direct Pay to pay your tax directly from your checking or savings account.
Generally, you must file Form 1040X within three years from the date you filed your original tax return or within two years of the date you paid the tax, whichever is later. For example, the last day for most people to file a 2014 claim for a refund is April 17, 2018. Special rules may apply to certain claims. Please call the office if you would like more information about this topic.
You can track the status of your amended tax return for the current year three weeks after you file. You can also check the status of amended returns for up to three prior years. To use the "Where's My Amended Return" tool on the IRS website, just enter your taxpayer identification number (usually your Social Security number), date of birth and zip code. If you have filed amended returns for more than one year, you can select each year individually to check the status of each.
Don't hesitate to call if you need assistance filing an amended return or have any questions about Form 1040X.
Tax Breaks for Businesses Hiring New Employees
If you're thinking about hiring new employees this year you won't want to miss out on tax breaks available to businesses with employees.
1. Payroll Tax Deduction for Startups
As part of the Research & Development Tax Credit, for tax years 2016 and beyond, startup businesses (C-corps and S-corps) with little to no revenue that qualify for the research and development tax credit can apply the credit against employer-paid Social Security taxes instead of income tax owed. Sole proprietorships, as well as Partnerships, C-corps and S-corps with gross receipts of less than $5 million for the current year and with no gross receipts for the previous year, can take advantage of the credit. Up to $250,000 in payroll costs can be offset by the credit.
2. Work Opportunity Credit
The Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) is a federal tax credit for employers that hire employees from the following targeted groups of individuals:
- A member of a family that is a Qualified Food Stamp Recipient
- A member of a family that is a Qualified Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) Recipient
- Qualified Veterans
- Qualified Ex-Felons, Pardoned, Paroled or Work Release Individuals
- Vocational Rehabilitation Referrals
- Qualified Summer Youths
- Qualified Supplemental Security Income (SSI) Recipients
- Qualified Individuals living within an Empowerment Zone or Rural Renewal Community
- Long Term Family Assistance Recipient (TANF) (formerly known as Welfare to Work)
The tax credit (a maximum of $9,600) is taken as a general business credit (Form 3800, General Business Credit), and is applied against tax liability on business income. It is limited to the amount of the business income tax liability or social security tax owed. Normal carryback and carryforward rules apply.
For qualified tax-exempt organizations, the credit is limited to the amount of employer social security tax owed on wages paid to all employees for the period the credit is claimed.
Also, an employer must obtain certification that an individual is a member of the targeted group before the employer may claim the credit.
Note: The Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes Act of 2015 (the PATH Act) retroactively allows eligible employers to claim the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) for all targeted group employee categories that were in effect prior to the enactment of the PATH Act, if the individual began or begins work for the employer after December 31, 2014 and before January 1, 2020.
For tax-exempt employers, the PATH Act retroactively allows them to claim the WOTC for qualified veterans who begin work for the employer after December 31, 2014, and before January 1, 2020.
3. Disabled Access Credit
Employers that hire disabled workers might also be able to take advantage of two additional tax credits in addition to the WOTC.
The Disabled Access Credit is a non-refundable credit for small businesses that incur expenditures for the purpose of providing access to persons with disabilities. An eligible small business is one that earned $1 million or less or had no more than 30 full-time employees in the previous year; they may take the credit each, and every year they incur access expenditures. Eligible expenditures include amounts paid or incurred to:
1. Remove barriers that prevent a business from being accessible to or usable by individuals with disabilities;2. Provide qualified interpreters or other methods of making audio materials available to hearing-impaired individuals;
3. Provide qualified readers, taped texts, and other methods of making visual materials available to individuals with visual impairments; or
4. Acquire or modify equipment or devices for individuals with disabilities.
4. Architectural Barrier Removal Tax Deduction
The Architectural Barrier Removal Tax Deduction encourages businesses of any size to remove architectural and transportation barriers to the mobility of persons with disabilities and the elderly. Businesses may claim a deduction of up to $15,000 a year for qualified expenses for items that normally must be capitalized. Businesses claim the deduction by listing it as a separate expense on their income tax return.
Businesses may use the Disabled Tax Credit and the Architectural/Transportation Tax Deduction together in the same tax year if the expenses meet the requirements of both sections. To use both, the deduction is equal to the difference between the total expenditures and the amount of the credit claimed.
5. State Tax Credits
Many states use tax credits and deductions as incentives for hiring and job growth. Employers are eligible for these credits and deductions when they create new jobs and hire employees that meet certain requirements. Examples include the New Employment Credit (NEC) in California, the Kentucky Small Business Tax Credit, and Empire Zone Tax Credits in New York.
6. FICA Tip Tax Credit
Certain food and beverage establishments can claim a credit for social security and Medicare taxes paid or incurred by the employer on certain employees' tips. The credit is part of the general business credit. To take advantage of this credit, restaurant managers must complete IRS Form 8846, Credit for Employer Social Security and Medicare Taxes Paid on Certain Employee Tips. If the restaurant employs more than 10 tipped employees, then IRS Form 8027, Employer's Annual Information Return of Tip Income and Allocated Tips is used to report tips and determine allocated tips for tipped employees. The credit is not refundable (there must be taxable income); however, unused FICA credits may be carried back one year or carried forward up to 20 years.
Questions?
If you're a business owner and are wondering what tax breaks your business qualifies for, don't hesitate to call the office and speak to a tax and accounting professional you can trust.
Seasonal Employees and Taxes
Many businesses hire part-time or full-time workers, especially in the summer. These types of employees are referred to as seasonal workers, which the IRS defines as an employee who performs labor or services on a seasonal basis (i.e., six months or less). Examples of this kind of work include retail workers employed exclusively during holiday seasons, sports events, or during the harvest or commercial fishing season. Part-time and seasonal employees are subject to the same tax withholding rules that apply to other employees.
All taxpayers fill out a W-4 when starting a new job. This form is used by employers to determine the amount of tax that will be withheld from your paycheck; however, Form W-4 worksheets filled out by many employees do not distinguish between part-year jobs and full-year jobs. Taxpayers (including students--more about this topic below) with multiple summer jobs will want to make sure all their employers are withholding an adequate amount of taxes to cover their total income tax liability.
Changes to Withholding under Tax Reform
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made changes to the tax law, including increasing the standard deduction, eliminating personal exemptions, increasing the child tax credit, limiting or discontinuing certain deductions and changing the tax rates and brackets starting in 2018.
Many taxpayers working part-time or who have seasonal jobs may not be aware of the changes in tax law that could affect their paycheck--and their 2018 tax returns when they file next year. Of note is that any changes a part-year employee makes to their withholding amount has a more significant impact on their paycheck than it does for employees who work year-round.
As such, now is a good time to perform a "paycheck check-up" using the Withholding Calculator, a special tool on the IRS website that can help taxpayers with part-year employment estimate their income, credits, adjustments, and deductions more accurately. It also checks to see whether a taxpayer is having the correct amount of tax withheld for their financial situation.
Using the withholding calculator
- First, the calculator asks about the dates of a taxpayer's employment and accounts for a part-year employee's shorter employment rather than assuming that their weekly tax withholding amount would be applied to a full year.
- Next, the calculator makes recommendations for part-year employees accordingly. If a taxpayer has more than one part-year job, the Withholding Calculator can account for this as well.
Taxpayers should have a completed 2017 tax return available and will also need their most recent pay stub before using the Withholding Calculator.
Calculator results depend on the accuracy of information entered. If a taxpayer's personal circumstances change during the year, they should return to the calculator to check whether their withholding should be adjusted. For taxpayers who work for only part of the year, it's best to do a "paycheck check-up" early in their employment period, so their tax withholding is most accurate from the start.
The Withholding Calculator does not request personally-identifiable information, such as name, Social Security number, address or bank account numbers. The IRS does not save or record the information entered on the calculator. As always, taxpayers should watch out for tax scams, especially via email or phone and be especially alert to cybercriminals impersonating the IRS. Remember, the IRS does not send emails related to the calculator or the information entered.
If you need to adjust your withholding
If the calculator results indicate a change in withholding amount, the employee should complete a new Form W-4 and should submit it to their employer as soon as possible. Employees with a change in personal circumstances that reduces the number of withholding allowances should submit a new Form W-4 with corrected withholding allowances to their employer within 10 days of the change.
As a general rule, the fewer withholding allowances an employee enters on the Form W-4, the higher their tax withholding will be. Entering "0" or "1" on line 5 of the W-4 means more tax will be withheld. Entering a bigger number means less tax withholding, resulting in a smaller tax refund or potentially a tax bill or penalty.
Students with Income from a Summer Job
If your child is a student with a summer job, the income your child earns over the summer is considered taxable income. For example, if your child is working as a waiter or a camp counselor, they may receive tips as part of their summer income. All tip income is taxable and is, therefore, subject to federal income tax.
Many students take on odd jobs over the summer to make extra cash. If this is your child's situation, keep in mind that earnings received from self-employment are also subject to income tax. This includes income from odd jobs such as babysitting and lawn mowing. If your child has net earnings of $400 or more from self-employment, they also have to pay self-employment tax. Church employee income of $108.28 or more must also pay self-employment tax. This tax pays for benefits under the Social Security system. Social Security and Medicare benefits are available to individuals who are self-employed just as they are to wage earners who have Social Security tax and Medicare tax withheld from their wages. The self-employment tax is figured on Form 1040, Schedule SE.
Generally, newspaper carriers or distributors under age 18 are not subject to self-employment tax; however, special rules apply to services performed as a newspaper carrier or distributor. As a direct seller, your child is treated as being self-employed for federal tax purposes if the following conditions are met:
- Your child is in the business of delivering newspapers.
- All pay for these services directly relates to sales rather than to the number of hours worked.
- Delivery services are performed under a written contract which states that your child will not be treated as an employee for federal tax purposes.
If your child participates in advanced training as an ROTC student and receives a subsistence allowance it is not taxable. Active duty pay, for example, pay received during a summer advanced camp, is taxable, however.
Help is just a phone call away.
As a seasonal or part-time worker, you may not be required to file a federal or state return if the wages you earn at a part-time or seasonal job are less than the standard deduction; however, if you work more than one job, you may end up owing tax. As you can see, seasonal and part-time workers have unique tax situations. If you have any questions about your tax situation, please call.
HSA Limits Increase for 2019
Contributions to a Health Savings Account (HSA) are used to pay current or future medical expenses of the account owner, his or her spouse, and any qualified dependent and are adjusted annually for inflation. For 2019, the annual inflation-adjusted contribution limit for a Health Savings Account (HSA) increases to $$3,500 for individuals with self-only coverage (up $50 from 2018) and $7,000 for family coverage (up $100 from 2018).
To take advantage of an HSA, individuals must be covered by a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) and not be covered by other health insurance with the exception of insurance for accidents, disability, dental care, vision care, or long-term care. Medical expenses such as deductibles, copayments, and other amounts (but excluding premiums) must not be reimbursable by insurance or other sources and do not qualify for the medical expense deduction on a federal income tax return.
For calendar year 2019, a qualifying HDHP must have a deductible of at least $1,350 for self-only coverage or $2,700 for family coverage (same as 2018) and must limit annual out-of-pocket expenses of the beneficiary to $6,750 for self-only coverage (up $100 from 2018) and $13,500 for family coverage (up $13,300 from 2018). As with contribution limits, deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses are adjusted for inflation annually.
Please call if you have any questions about Health Savings Accounts.
New Scam Targets Non-resident Aliens
In yet another new twist on an old scam--this time affecting non-resident aliens and international taxpayers--criminals are using a fake IRS Form W-8BEN to solicit detailed personal identification and bank account information from victims. Here's how the scam works:
1. Criminals mail or fax a letter indicating that although individuals are exempt from withholding and reporting income tax, they still need to authenticate their information by filling out a phony version of Form W-8BEN, Certificate of Foreign Status of Beneficial Owner for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting.
2. Recipients are then asked to fax the information back to the scammers.
3. While Form W-8BEN is a legitimate U.S. tax exemption document, it can only be submitted through a withholding agent. A withholding agent may be an individual, corporation, partnership, trust, association, or any other entity, including any foreign intermediary, foreign partnership, or U.S. branch of certain foreign banks and insurance companies.
4. In the past, fraudsters have targeted non-residents of the U.S. using Form W-8BEN as a lure to get personal details such as passport numbers and PIN codes. IRS Form W-8BEN does not ask for any of that information. The phony letter or fax also refers to a Form W9095, which does not exist. Furthermore, the IRS doesn't require recertification of foreign status.
Scam variations
Non-resident alien and international taxpayers should be alert to bogus letters, emails, and letters that appear to come from the IRS or your tax professional requesting information. Scam letters, forms, and e-mails are designed to trick taxpayers into thinking these are official communications from the IRS or others in the tax industry, including tax software companies. These phishing schemes may seek personal information, including mother's maiden name, passport, and account information in order steal the victim's identity and their assets.
Remember, the IRS does not:
- Demand that people use a specific payment method, such as a prepaid debit card, gift card or wire transfer.
- Ask for debit or credit card numbers over the phone.
- Demand immediate tax payment. Normal correspondence is a letter in the mail and taxpayers can appeal or question what they owe.
- Threaten to bring in local police, immigration officers or other law enforcement to arrest people for not paying.
- Revoke a license or immigration status. Threats like these are common tactics scam artists use to trick victims into believing their schemes.
If you have been a victim of an IRS phone scam or any IRS impersonation scam, please contact the office immediately. You should also report it to the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration at its IRS Impersonation Scam Reporting site and to the IRS by emailing [email protected] with the subject line "IRS Impersonation Scam."
What to do if you get a Letter from the IRS
Each year, the IRS mails millions of notices and letters to taxpayers for a variety of reasons. If you receive correspondence from the IRS here's what to do:
Don't panic. You can usually deal with a notice simply by responding to it. Most IRS notices are about federal tax returns or tax accounts.
Each notice has specific instructions, so read your notice carefully because it will tell you what you need to do.
Your notice will likely be about changes to your account, taxes you owe or a payment request. However, your notice may ask you for more information about a specific issue.
If your notice says that the IRS changed or corrected your tax return, review the information and compare it with your original return. If you agree with the notice, you usually don't need to reply unless it gives you other instructions or you need to make a payment.
If you don't agree with the notice, you need to respond. Write a letter that explains why you disagree and include information and documents you want the IRS to consider. Mail your response with the contact stub at the bottom of the notice to the address on the contact stub. Allow at least 30 days for a response.
For most notices, there is no need to call or visit a walk-in center. If you have questions, call the phone number in the upper right-hand corner of the notice. Be sure to have a copy of your tax return and the notice with you when you call. If you need assistance understanding an IRS Notice or letter, don't hesitate to call the office.
Always keep copies of any notices you receive with your tax records.
Be alert for tax scams. The IRS sends letters and notices by mail and does NOT contact people by email or social media to ask for personal or financial information. If you owe tax, please call to find out what your options are.
Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Program to End this Year
U.S. taxpayers with undisclosed foreign financial assets should take advantage of the Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Program (OVDP) before the program closes on September 28, 2018. The planned end of the current OVDP also reflects advances in third-party reporting and increased awareness of U.S. taxpayers of their offshore tax and reporting obligations.
More than 56,000 taxpayers have used one of the programs to voluntarily comply since the OVDP's initial launch in 2009, paying a total of $11.1 billion in back taxes, interest, and penalties. The number of taxpayer disclosures under the OVDP peaked in 2011 when about 18,000 people came forward; however, the number steadily declined through the years, falling to only 600 disclosures in 2017.
The current OVDP began in 2014 and is a modified version of the OVDP launched in 2012, which followed voluntary programs offered in 2011 and 2009. The programs have enabled U.S. taxpayers to voluntarily resolve past non-compliance related to unreported foreign financial assets and failure to file foreign information returns.
Tax Enforcement
Stopping offshore tax noncompliance remains a top priority of the IRS and taxpayers should note that the IRS will continue to use other tools besides voluntary disclosure to combat offshore tax avoidance such as taxpayer education, Whistleblower leads, civil examination and criminal prosecution.
Since 2009, IRS Criminal Investigation has indicted 1,545 taxpayers on criminal violations related to international activities and remains actively engaged in ferreting out the identities of those with undisclosed foreign accounts with the use of information resources and increased data analytics, according to Don Fort, Chief, IRS Criminal Investigation.
Streamlined Procedures and Other Options
A separate program, the Streamlined Filing Compliance Procedures, for taxpayers who might not have been aware of their filing obligations, has helped about 65,000 additional taxpayers come into compliance. The Streamlined Filing Compliance Procedures will remain in place and available to eligible taxpayers; however, the program may end at some point.
The implementation of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) and the ongoing efforts of the IRS and the Department of Justice to ensure compliance by those with U.S. tax obligations have raised awareness of U.S. tax and information reporting obligations with respect to undisclosed foreign financial assets. Because the circumstances of taxpayers with foreign financial assets vary widely, the IRS will continue offering the following options for addressing previous failures to comply with U.S. tax and information return obligations with respect to those assets:
- IRS-Criminal Investigation Voluntary Disclosure Program;
- Streamlined Filing Compliance Procedures;
- Delinquent FBAR submission procedures; and
- Delinquent international information return submission procedures.
For more information about the options available for U.S. taxpayers with undisclosed foreign financial assets, please contact the office.
Employer Credit for Family and Medical Leave
Thanks to the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act last year, there's a new tax benefit for employers: the employer credit for paid family and medical leave. As the name implies, employers may claim the credit based on wages paid to qualifying employees while they are on family and medical leave.
Here are six facts about this credit and how it benefits employers:
1. To claim the credit, employers must have a written policy that meets certain requirements such as:
- Employers must provide at least two weeks of paid family and medical leave annually to all qualifying employees who work full time. This can be prorated for employees who work part-time.
- The paid leave must be not less than 50 percent of the wages normally paid to the employee.
2. A qualifying employee is any employee who has been employed for one year or more, and for the preceding year, had compensation that did not exceed a certain amount. For employers to take this credit in 2018, the employee must not have earned more than $72,000 in 2017.
3. "Family and medical leave" as defined for this particular credit, is leave that is taken for one or more of the following reasons:
- Birth of an employee's child and to care for the newborn.
- Placement of a child with the employee for adoption or foster care.
- To care for the employee's spouse, child, or parent who has a serious health condition.
- A serious health condition that makes the employee unable to perform the functions of his or her position.
- Any qualifying event due to an employee's spouse, child, or parent being on covered active duty - or being called to duty - in the Armed Forces.
- To care for a service member who is the employee's spouse, child, parent, or next of kin.
4. The credit is a percentage of the amount of wages paid to a qualifying employee while on family and medical leave for up to 12 weeks per taxable year.
5. To be eligible for the credit, an employer must reduce its deduction for wages or salaries paid or incurred by the amount determined as a credit. Any wages taken into account in determining any other general business credit may not be used toward this credit.
6. The credit is generally effective for wages paid in taxable years of the employer beginning after December 31, 2017. It is not available for wages paid in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2019.
For more information about the employer credit for family and medical leave, please contact the office.
Customize QuickBooks' Forms
Every opportunity you have to interact with your customers and vendors is critical. Whether it's a phone call, an in-person connection, or an email, how you present yourself reveals a lot about you. Are you efficient? Friendly? Do you handle orders and problems and payment issues quickly and carefully?
Your accounting forms can also contribute to your image. They should always be:
- Neat and attractive.
- Easy to read, with the most important information displayed prominently.
- Consistent with any graphics you use on other company materials.
- Accurate, above all.
You might be able to use at least some of QuickBooks' form templates as is, without any modifications. But couldn't they be better? More visually appealing? Formatted to include only the fields that your business most often needs? QuickBooks contains the customization tools you need to make them so.
Improving What Exists
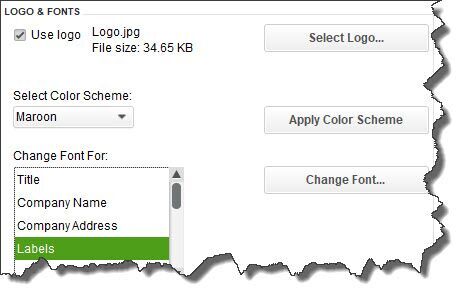
Figure 1: You can personalize your QuickBooks forms and make them consistent with any design themes your brand may use.
Let's look at the modification options for an invoice, though, depending on what version of QuickBooks you're using, you can also work with sales receipts, purchase orders, statements, estimates, sales orders, and credit memos. Start by opening the Lists menu and selecting Templates. Highlight Intuit Product Invoice in the list. Click the down arrow next to Templates in the lower left corner and choose Edit Template.
The above image displays part of the window that opens. Here, you can add a logo, change the color scheme, and change fonts for your company's contact information and the labels that identify each field (like Bill To, Terms, and Quantity). The right pane of this window shows you what the form will look like as you make changes.
Nothing you've done so far will prevent you from using Intuit's pre-printed forms. But when you click Additional Customization at the bottom of the screen, you'll be warned that if you make modifications beyond this point, the forms may not print correctly. To be safe, click Make a Copy. You'll be able to print this new version on plain paper.
Deeper Customization
The image below shows you part of the window that opens when you click on Additional Customization. The first two columns here are the most important; they let you specify the labeled fields that will appear on your invoices. When Header is the active column, you'll be able to choose the content that will go at the top of your form, like Date, Invoice Number, and Terms.
Next to each default label, you'll see boxes for Screen and Print. Click in these boxes to create or delete checkmarks; this will indicate whether each label will appear in the software itself and which will be printed for your customers to see. If you'd like to change the language QuickBooks uses to describe each, enter your preferred word or phrase in the Title column.
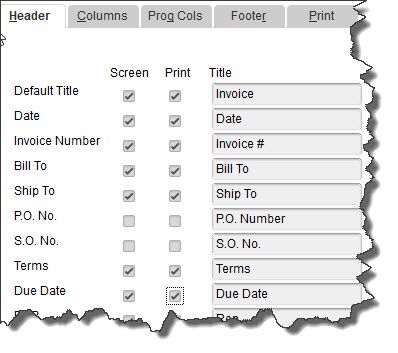
Figure 2: With the Header column highlighted, you can shape the appearance of the top section of your invoices.
Caution: As you're checking and unchecking boxes, a dialog box may open telling you that your changes will cause some fields to overlap on your form. If you click the Default Layout button, QuickBooks will make automatic adjustments to fix this. Clicking Continue means you'll have to use the software Layout Designer to make your own adjustments. This tool is not particularly intuitive, and it requires some design skills. If you must work with the Layout Designer, please call for assistance.
When you click the Columns tab, you'll see a list of the fields available for the main body of your invoices, like Description, Quantity, and Rate. This works similarly to how you just modified the Header, with one exception: You'll be able to enter numbers in the Order column to specify the placement of each field. Here again, you'll be able to watch a preview of your form change in the right pane.
If you want to start over, click the Default button to revert the form to its original state. When you're done, click OK.
Neatness Counts
Whether you print and mail your forms or simply dispatch them electronically, we strongly encourage you to make them as professional and polished as you possibly can. Their appearance will enhance or detract from the image your customers and vendors have of your business. Please call the office if you need help learning about and implementing the customization options that QuickBooks offers.
Tax Due Dates for June 2018
June 11
Employees who work for tips - If you received $20 or more in tips during May, report them to your employer. You can use Form 4070.
June 15
Individuals - If you are a U.S. citizen or resident alien living and working (or on military duty) outside the United States and Puerto Rico, file Form 1040 and pay any tax, interest, and penalties due. U.S. citizens living in the U.S. should have paid their taxes on April 17. If you want additional time to file your return, file Form 4868 to obtain 4 additional months to file. Then file Form 1040 by October 15. However, if you are a participant in a combat zone, you may be able to further extend the filing deadline.
Individuals - Make a payment of your 2018 estimated tax if you are not paying your income tax for the year through withholding (or will not pay enough tax that way). Use Form 1040-ES. This is the second installment date for estimated tax in 2018.
Corporations - Deposit the second installment of estimated income tax for 2018. A worksheet, Form 1120-W, is available to help you estimate your tax for the year.
Employers - Nonpayroll withholding. If the monthly deposit rule applies, deposit the tax for payments in May.
Employers - Social Security, Medicare, and withheld income tax. If the monthly deposit rule applies, deposit the tax for payments in May.
Do you have any questions? Contact Paramount Tax today, we're happy to help!


